TL;DR
Algorand was founded in 2017 before launching its mainnet and ALGO token in June 2019. The blockchain deals with the common scalability and consensus mechanism issues common to first and second-generation blockchains. Algorand's main feature is its Pure Proof of Stake consensus protocol that randomly selects validators weighted by their staked ALGO coin.
Users who stake their ALGO have the chance of being selected to propose and validate a new block, which is then verified by a randomly-selected committee. Once the block is added to the blockchain, all transactions are considered confirmed. If the block is deemed bad, a new user is selected as a validator, and the process starts again.
The system's main strength is its decentralization of power, as every single staker has the chance to be a validator. Apart from consensus, ALGO is also used for network transaction fees and to earn block rewards. If you want to buy or sell ALGO, you can easily do so through Binance's convert feature or exchange view.
Introduction
Algorand is a fairly new blockchain focused on improving scalability without sacrificing decentralization. This problem is common to many of the first and second-generation blockchains, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. To achieve this, Algorand developed perhaps its most notable feature: the Pure Proof of Stake (PPoS) consensus mechanism. Along with its passive staking, both of these features have made Algorand a large market cap project popular with users seeking rewards.
What is Algorand?
What is the Algorand Foundation?
For example, the Foundation has educated developers in universities and supported Algorand projects in its ecosystem with accelerator programs. However, technical development work is carried out by the private company Algorand Inc. The Algorand Foundation is also a large holder of ALGO, which it uses to fund its activities.
How does Algorand work?
Proposal step
Once users have staked and generated their participation key, they become participation nodes. Communication between these nodes happens through Algorand relay nodes. The block proposal phase then selects multiple block proposers using a Verifiable Random Function (VRF), considering the proportion of each validator's stake. Once block proposers are chosen, their identity is kept secret until the new block is proposed. This improves network security as bad actors cannot maliciously target the chosen validator. However, a proposer can demonstrate their VRF output along with their proposed block to prove their legitimacy.
Soft vote stage
Certify vote stage
What is ALGO?
ALGO is the native coin of Algorand and has a maximum total supply of 10 billion coins to be distributed by 2030. New ALGO is sent to specific ALGO-holding wallets with each newly forged block. You need to hold at least 1 ALGO in a non-custodial wallet to receive these ALGO rewards. This reward can generate an APY of around 5-8% for ALGO holders and is distributed roughly every 10 minutes. This mechanism makes the ALGO coin one of the simplest cryptocurrencies to generate a passive income with, as you can "passively stake" the token.
What are ALGO’s use cases?
Like many other native coins, ALGO has three primary use cases:
2. ALGO can be staked to have a chance of being selected as a block proposer or validator.
How to Buy ALGO on Binance
You can purchase ALGO on Binance in just two steps with a credit or debit card. If you already have crypto in your account, you may be able to swap directly for ALGO if it's in a pair with the coin you hold. To begin, let's look at using a credit or debit card.
1. Log in to your Binance account and hover over the [Buy Crypto] header at the top left of the homepage. In the drop-down menu, select [Credit/Debit Card].
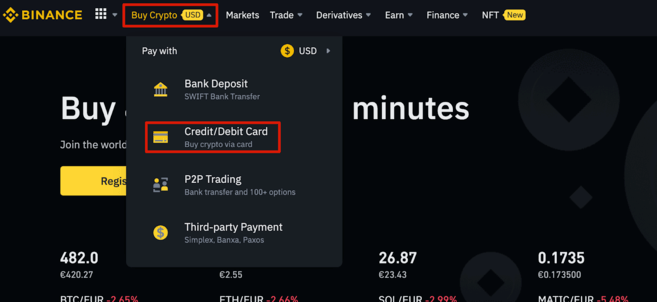
2. Next, select the fiat currency you'll pay with your card in the top field. In the bottom field, choose your desired cryptocurrency. Make sure that it is in a pair with ALGO to trade for it directly.
3. Click [Continue] and accept any terms and conditions if it's your first time purchasing with fiat.
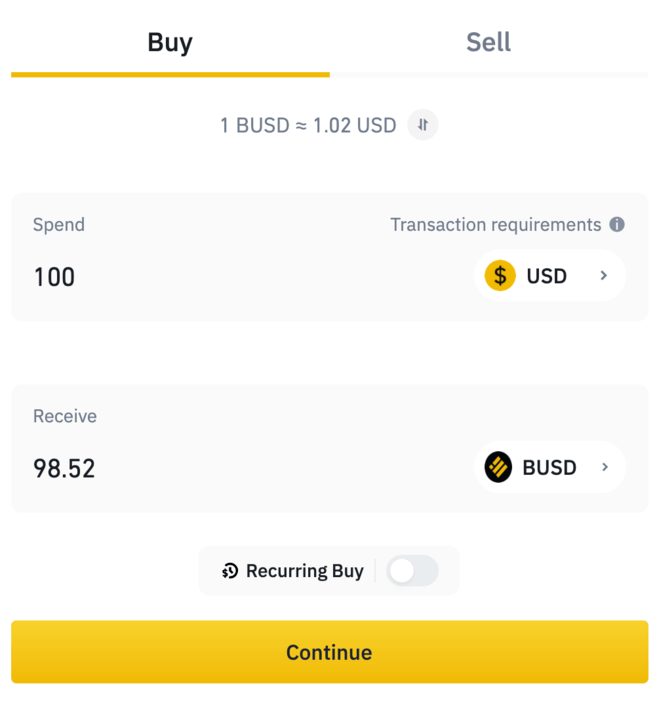
4. Click [Add new card] or select a card already added to your account, and then follow the instructions for completing your payment.

5. Now, you'll need to swap your BUSD for ALGO. You can do this easily with the [Convert] feature accessible under the [Trade] header.

6. Select the crypto you want to convert from in the top field and ALGO in the bottom. If you cannot see ALGO in the bottom field, it is not in a trading pair with your chosen crypto. Click [Preview Conversion] after entering the amount you want to swap.
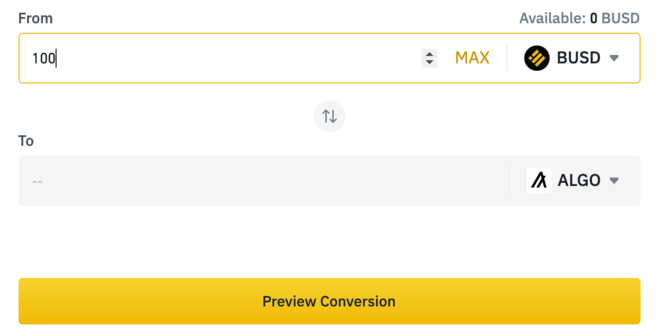
7. You'll now see a preview of the amount of ALGO you'll receive with clear instructions on how to proceed. Once you have swapped, the ALGO will be in your Spot Wallet.

8. You can also trade using the Classic or Advanced exchange view. By hovering over the currently displayed pair, you can search for all available ALGO pairs.

How to Sell ALGO on Binance
1. To sell ALGO, you can use the Convert feature again. This time, select ALGO in the top field and the cryptocurrency you want to convert to at the bottom. Click [Preview Conversion] to check the exchange rate.
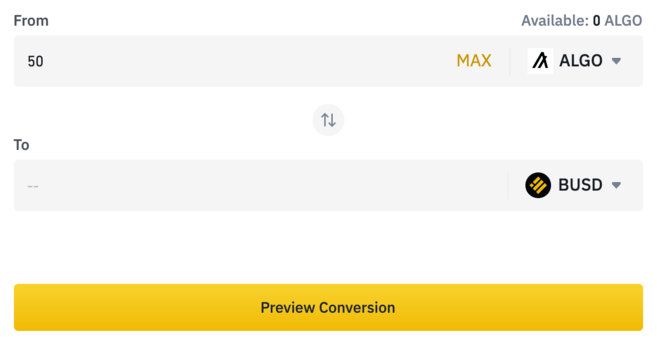
2. Once you've confirmed the amount you'll receive, follow the instructions given to finalize your trade.

3. You can then convert to fiat using the same process so long as the coin you traded your ALGO for is in a fiat pair.
Conclusion
Like other alternative blockchains to Bitcoin and Ethereum, Algorand has focused heavily on scalability and decentralization. Its Pure Proof of Stake consensus mechanism provides a unique solution with VRFs, and many find this blockchain technology attractive for its success in decentralizing power.










![Warsaw Stock Exchange: Brand24 (B24) - 1Q23 financial results Turbulent Q2'23 Results for [Company Name]: Strong Exports Offset Domestic Challenges](/uploads/articles/2022-FXMAG-COM/GPWA/gpw-s-analytical-coverage-support-programme-wse-2-6311cd4191809-2022-09-02-11-30-41-63175bda84812-2022-09-06-16-40-26.png)









![Warsaw Stock Exchange: Brand24 (B24) - 1Q23 financial results Turbulent Q2'23 Results for [Company Name]: Strong Exports Offset Domestic Challenges](https://www.fxmag.com/media/cache/article_small_filter/uploads/articles/2022-FXMAG-COM/GPWA/gpw-s-analytical-coverage-support-programme-wse-2-6311cd4191809-2022-09-02-11-30-41-63175bda84812-2022-09-06-16-40-26.png)


